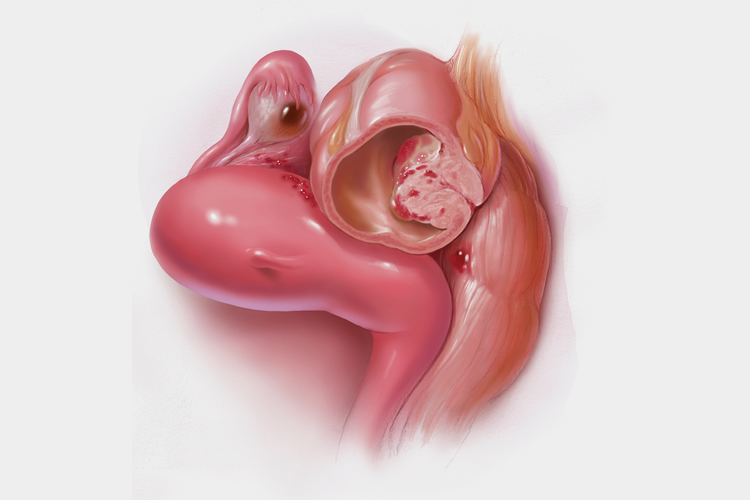
| Prevalence | 1 out of 5 endometriosis cases infiltrate deeper into the large and small intestine. |
Area of Involvement:
90% of bowel endometriosis cases involve the rectum and sigmoid colon, while 10% involve the appendix and ileum. Patients with bowel disease also have a higher chance of developing diaphragmatic endometriosis. Advanced bowel disease–requiring nodule excision or bowel resection procedures–involves the urinary system also, including the ureters and bladder. Approximately 15-20% of bowel endometriosis are multi-focal (diffuse within a certain area), while the rest are multi-centered.
Symptoms of bowel endometriosis
- painful bowel movements, rectal pain, and bowel spasms specifically increasing during periods
- blood stained stools during periods
- constipation, especially during periods
- alternating diarrhea and constipation (some patients have diarrhea first then constipation, while others have the reverse) during menses
- abnormal gas, especially during periods
- abdominal bloating
- Painful sex (dyspareunia), due to infiltration of endometriosis to the rectum and pouch of Douglas
- Irritable bowel syndrome worsening around the time of menses
As most of the symptoms of bowel endometriosis include digestive or gastrointestinal pain, it is commonly misunderstood as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). The only difference is in the frequency and severity of pain in endometriosis related IBS. A woman with pure IBS without endometriosis may experience pain several times per week and any day of the month, while bowel endometriosis causes intense pain specifically around timing of the menstrual cycle.